Types of Innovation
Innovation is a term with a huge variety of definitions. Written definitions focus on various different aspects which some models try to summarize and visualize that are discussed below.
In general, the majority of these definitions and models can be categorized into the following three areas:

- Sources of Innovaiton
- What are the roots of innovation processes and activities? Who or what triggers innovation within an organization or society?
- Objects of Innovation
- What are the objects that are going to be changed and/or enhanced during the innovation processes?
- Impact of Innovation
- What is the impact of the innovation activities looking at the corporation and the whole market?
As shown in the visualization for these three categories of innovation models, these models are not exhaustive as they are focussing on specific aspects of innovation rather than the whole process or outcome. However, all of these models cover valuable parts of a comprehensive innovation definition, which is why taking a deep dive into each of these categories is crucial to have a holistic view on innovation.
Sources of Innovation
The 5 Types of Innovation model covers the sources of innovations. It aims at structuring the different internal and external sources a corporation can utilize in order to foster innovation.
5 Types of Innovation
- Employee Innovation
- start from within: based on collective wisdom of many
- Customer Innovation
- interaction: talk to your customers
- Partner/Supplier Innovation
- collaborate: form alliances
- Competitor Innovation
- scale: establish formal programs
- Public Innovation
- open up: invite the public to join
Objects of Innovation
The following two models focus on the objects that are going to be affected by innovation activities.
Since there are endless possibilities of objects/processes/products/services that can be innovated, these models can never cover all of them. However, understanding the idea behind looking at the affected objects with the examples given in these models, one can easily adapt these models to one’s own corporate landscape.
3 Types of Innovation
- Product Innovation
- Process Innovation
- Business Model Innovation
6 Types of Innovation
- Product
- Service
- Process
- Management
- Open
- Value
Impact of Innovation
The most interesting and widely known and discussed model for categorizing innovation is the “4 Types of Innovation” model. Instead of simply listing bullet points it allows to categorize innovations on a two-dimensional scale:
- Newness of Technology
- Most innovations incorporate a new technology which enables these innovations to either gradually improve existing processes and products or radically disrupt by the use of a whole new technology that acts as a gamechanger by being dramatically differnt to the previously used technology. Most often, new technologies enable executions that have not been able with existing technology.
- Impact on Market
- The impact on the market can be low and thus affecting the corporation itself rather than the market the corporation acts within. These innovations can be radical to the corporation by e.g. changing production processes but do not affect the market as they are only internal innovations.
- On the other hand, innovations are able to be disruptive by mixing up the whole market having a huge impact not only on the company itself but also the competition. Sometimes these innovations even change how a market functions by introducing new business models that force existing business models to become obsolete.
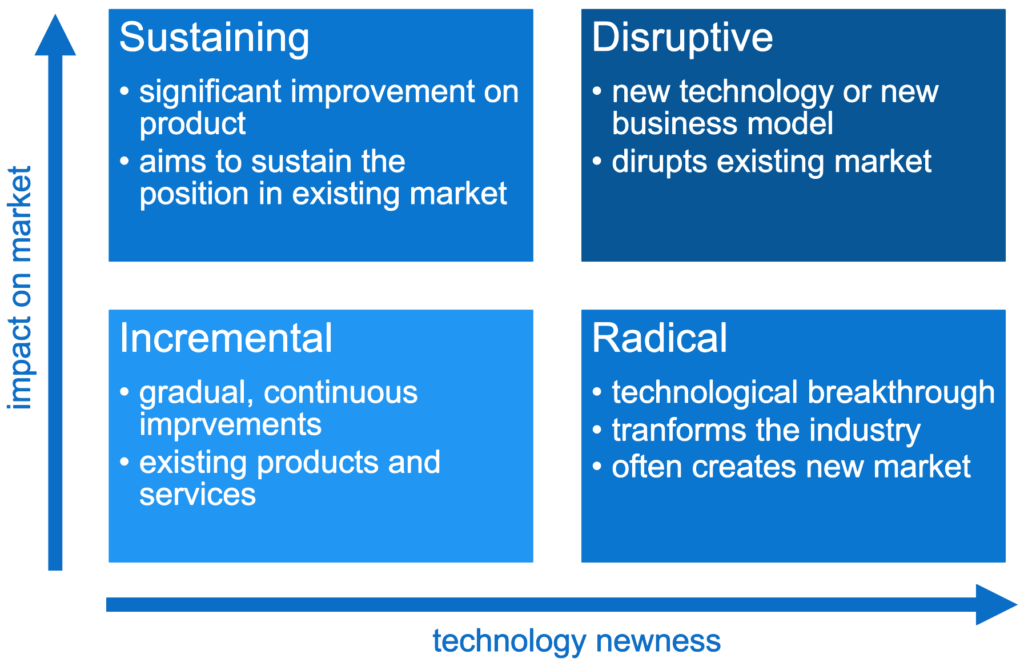
Incremental Innovations
- Low technology newness, low impact on market
- Incremental innovations are very gradual. They only add a small continuous improvement on existing products or services and thereby only have little impact on the external market. It is debatable whether incremental innovations are true innovations or simply incremental improvements that a corporation generally faces while developing products further.
Sustaining Innovations
- Low technology newness, high impact on market
- Sustaining innovations are significant improvements to a product or service that aim to sustain the position of the product/brand/company within an existing market. They are capable of gaining a compatitive advantage among the competitors without introducing new technology.
Radical Innovation
- High technology newness, low impact on market
- Radical innovations introduce a new technology due to a technological breakthrough. This breakthrough has the potential to transform an industry by creating a new market that has not exist before rather than disrupting existing markets.
Disruptive Innovations
- High technology newness, high impact on market
- Disruptive improvements introduce new technology to an existing market and thereby disrupting the existing competition. The impact on the market is so high, that disruptiv innovatoins force competitors to catch up on the new technologies in order to maintain their position in the market.
Conclusion
As shown above, there are various ways to structure and differentiate types of innovation. While most of them focus on specific aspects of innovation activities, it is beneficial to keep in mind that some models are more suitable to classify your innovation activities than others. All things considered, taking a look at the three different categorizations of innovation models (source, object, impact) will help to not lose track of any of these fields. Thus ensuring to have a reasonable cause (source), tackle the right assets (object), and deliver sustainable value (impact) with your innovation activities.

Comments 1
Pingback: Designing an innovation process from scratch – a blueprint. | Intrapreneur.Tools